Last Updated: 2/6/2023
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence, also known as AI is a rapidly growing field that is changing the way we live and work. But what exactly is AI, and how does it work?
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI for short, is the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think and learn like humans. These machines use algorithms and data to make decisions, solve problems, and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks can include understanding natural language, recognizing images, playing games, and even driving cars.
One of AI's key elements is the machine's ability to learn and improve over time. This is known as machine learning, but we will discuss it later.
The term Artificial Intelligence or AI appeared for the first time in 1995 when emeritus Stanford Professor John McCarthy defined it as:
"the science and engineering of making intelligent machines" — John McCarthy, 1995.
However, almost 60 years before McCarthy, Alan Turing thought computers could do more than execute instructions. Turing believed that one day, computers would be able to figure out those instructions independently.
“could a computer go beyond “what we know how to order it to perform” and learn on its own how to perform a specified task. Could a computer surprise us? Rather than programmers crafting data-processing rules by hand, could a computer automatically learn these rules by looking at data?” — Alan Turing, 1938.
Artificial Intelligence is much more complex than it seems at first glance, and many companies misuse it or confuse it with Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Artificial Intelligence
Field of computer science related to understanding and building intelligent entities capable of simulating human reasoning and behavior.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the idea of making machines that can think and act like humans. Essentially, it’s a type of computer programming that allows computers to learn and perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence.
For example, an AI system might be trained to recognize objects in an image or translate spoken words into text. It does this by processing vast amounts of data and using algorithms to make decisions based on that information. The more data an AI system has access to, the more it can learn and improve.
There are different types of AI, including machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and more. Machine learning involves teaching a computer to learn from data, deep learning involves using neural networks to teach computers to recognize patterns, and natural language processing involves making computers understand and generate human language.
The goal of AI is to make machines that can work alongside humans and help us solve complex problems more efficiently. Although we are still far from creating truly intelligent machines, the field of AI is rapidly advancing and has the potential to greatly impact our lives in the future.
How does Artificial Intelligence work?
Think of AI as a chef who has to make a new dish. The chef has a recipe book, which is like the algorithms in an AI system. The recipe book tells the chef what ingredients to use and how to combine them to make the dish. But, instead of a recipe book, an AI system has access to vast amounts of data. This data is like the ingredients the chef uses to make the dish. The AI system uses algorithms to analyze the data and make decisions, just like the chef uses the recipe book to make the dish. However, unlike a recipe book, the AI system can also learn and improve over time. The more data it processes, the more it can learn and make better decisions. So, if the chef keeps trying different recipes and adjusting the ingredients, he can eventually create a new and improved dish. In the same way, an AI system can continuously improve its performance by processing more data and learning from its mistakes. This is why AI systems can become very good at performing certain tasks, like recognizing faces in images or translating spoken words into text.
Where is AI being used today?
Artificial Intelligence is being used in a wide range of industries and applications today, including:
- Healthcare; where it is being used to assist in medical diagnoses, create personalized treatment plans, and even perform surgeries.
- Transportation. Self-driving cars use AI to navigate and make decisions on the road.
- Finance. AI is being used to detect fraud and make investment decisions.
- Retail; for personalization of shopping experiences, predicting consumer behavior and inventory management.
- Agriculture: AI used for precision farming and yield prediction.
- Manufacturing: for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization The list of applications and new technologies increases every year.
Artificial Intelligence sub-fields
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field that contains many different sub-disciplines and approaches. Some standard divisions within AI include:
- Machine Learning. This type of AI allows systems to learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning techniques include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Deep Learning or Neural Networks: This is one if not the most popular sub fields of AI. Inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, Neural Networks process information using interconnected layers of nodes. Neural networks are used for a wide range of tasks, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and game playing.
- Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning in which the computer learns by taking actions in an environment and receiving rewards or penalties for those actions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is the study of how computers can understand and generate human language, such as speech recognition, translations, and machine translation. NLP techniques are used to understand and generate human languages.
- Computer Vision (CV): This is the study of how computers can interpret and understand visual data, such as images and videos. Computer vision techniques are used in object recognition, image segmentation, and facial recognition.
- Robotics: This is the study of how to design and control robots, which are machines that can mimic human actions and behavior. Robotic techniques are used to control robots' movement and sense and develop intelligent behaviors for them.
- Expert Systems: These are computer programs that mimic the decision-making abilities of human experts in a specific field. They use knowledge and rule-based systems to solve complex problems and make decisions.
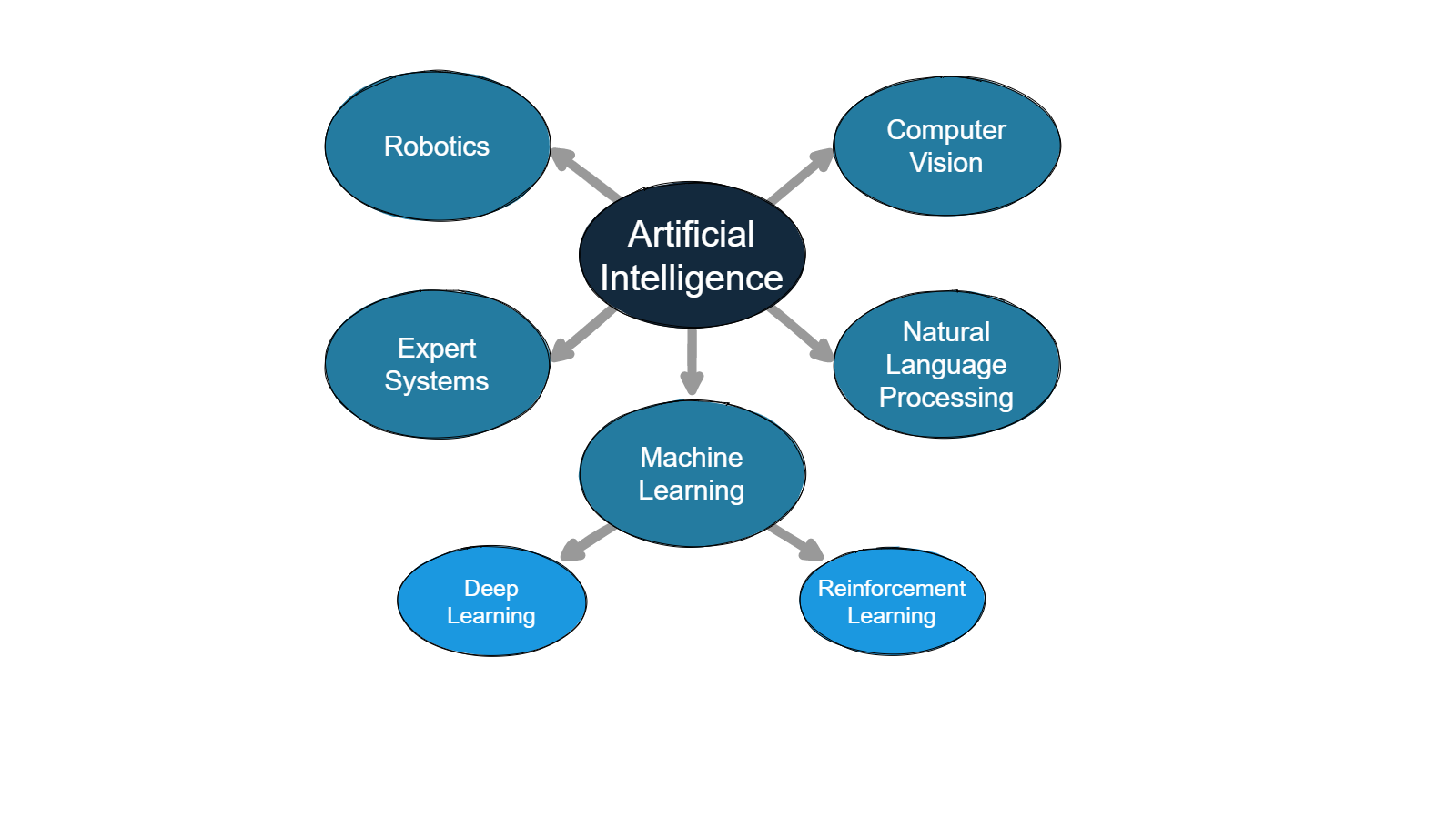
These are just some examples of many different subfields within AI. Research in AI is constantly evolving and new subfields are emerging as new technologies and approaches are developed.
Levels of Artificial Intelligence
There are several different ways to categorize the levels of Artificial Intelligence (AI), but one commonly used framework is based on the capabilities of the AI system. These levels are:
- Reactive Machines: These are the simplest type of AI systems. They can only react to the current situation, don't have memory, and can't use past experiences to inform current decision-making. An example of this type of AI is IBM's Deep Blue, the chess-playing computer that defeated the world champion in 1997.
- Limited Memory: This type of AI system have memory, it can store and recall past experiences to inform current decision-making, but it can't use that information to form an understanding of the world. An example of this type of AI is self-driving cars that use cameras and sensors to detect their surroundings and make decisions based on that information.
- Theory of Mind: This type of AI system can reason. They also understand emotions, beliefs, and intentions. But this type of AI technology is still in the research stage and isn't practical yet.
- Self-Aware: This is the most advanced type of AI. It can be self-aware and understand its consciousness. This is still a topic of debate and research in the field, and it's still being determined if this level will ever be reached.

Extra Resources
Books
Chapter 2: You’ll learn about the Turing test in the second chapter.
Chapter 3: In this chapter, you’ll learn about the limitations of Artificial Intelligence.
Videos
Motivational